Introduction
With the adoption of the NIS2 Directive, the European Union is strengthening the cybersecurity of its member states, and kicking off the digital security and digital autonomy of European organizations. The NIS2 Directive builds on the foundations of its predecessor, the NIS, by broadening its objectives and scope to include a greater number of entities insufficiently protected against cyber risks. It emphasizes enhanced cooperation between member states, notably through the CyCLONe network, for more effective management of cyber crises.

Legislative framework and evolution of the NIS2 Directive
The NIS2 Directive, adopted on December 14, 2022, under the official name of Directive (EU) 2022/2555, strengthens cybersecurity in the European Union. It succeeds the NIS Directive.
It broadens its scope, introduces enhanced requirements and categorizes entities as “essential” and “important”, covering various sectors such as energy, transport, healthcare and digital, to ensure uniform security in the face of cyber threats.

NIS2 also highlights the need for regulatory harmonization across the Union, aimed at avoiding disparities between member states in terms of preparedness and response to cyber threats. This consistency is crucial to Europe’s overall resilience to cybersecurity incidents, as vulnerabilities in a single member state can have repercussions across borders.
“The requirements set out in the European directive call on many entities to build a solid roadmap for deploying and strengthening their cyber defense resources, with the objectives of safer structural operation, greater confidence vis-à-vis their stakeholders, and improved competitiveness for businesses. Ultimately, and in concert with the other member states of the European Union (EU), it is a Europe-wide cyber maturity that we want to achieve. “
Vincent Strubel, Director General, French National Agency for Information Systems Security (ANSSI)
Analysis of security requirements under NIS2
Under NIS2, essential and important entities must take at least the following measures:
- Risk analysis and information systems security policies.
- Incident management (prevention, detection and response).
- Business continuity and crisis management.
- Supply chain security.
- Security in the acquisition, development and maintenance of networks and information systems, including vulnerability management and disclosure.
- Policies and procedures (tests and audits) to assess the effectiveness of cybersecurity risk management measures.
- Basic cybersecurity hygiene practices and training.
- Policies and procedures concerning the use of cryptography and, if necessary, encryption.
- Human resources security, access control policies and asset management.
- Use of multi-factor authentication or continuous authentication solutions, secure video, voice and text communication systems, and secure emergency communication.
These technical and organizational measures aim to strengthen the security posture of entities, enabling them to effectively prevent, detect and respond to cyber threats. They create defense-in-depth, ensuring greater preparedness and resilience in the face of cybersecurity incidents.

NIS2 is to be implemented alongside other European regulatory frameworks, including the RGPD, which protects personal data, and the DORA Directive, which strengthens the digital resilience of financial services. Together, these regulations create a data security and protection ecosystem that ensures integrated risk management.
How does PARSEC contribute to your response to NIS2?
NIS2 must be implemented to complement other European regulatory frameworks, especially the RGPD, which protects personal data, and the DORA Directive, which strengthens the digital resilience of financial services. Together, these regulations create a data security and protection ecosystem that ensures integrated risk management

Incident Management and Notification under NIS2
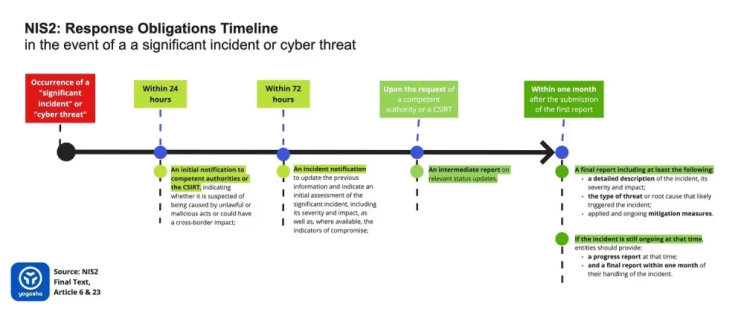
A central aspect of NIS2 is its rigorous incident reporting framework, which requires affected entities to report any significant incident within specific timeframes. The directive stipulates early warning within 24 hours of discovery of the incident, and full notification within 72 hours. This multi-stage process is designed to ensure a rapid response to cybersecurity incidents, thus minimizing their potential impact.
The directive also requires entities to adopt measures to inform stakeholders and, where appropriate, the general public, in the event of significant incidents. This transparency is crucial to maintaining trust in digital services and to helping users take appropriate action in response to incidents.
Sanctions and Compliance Obligations
The NIS2 Directive introduces severe penalties for entities that fail to comply with cybersecurity requirements.
Les amendes peuvent atteindre jusqu'à 10 millions d'euros ou 2 % du chiffre d'affaires annuel mondial, selon le montant le plus élevé. These sanctions are designed to ensure that entities take their cybersecurity obligations seriously and implement the necessary measures to protect their information systems.
In addition, the directive imposes strict compliance obligations, requiring entities to demonstrate their compliance to regulatory authorities. This includes carrying out regular audits, implementing robust security policies and providing ongoing cybersecurity training for employees. Entities must also maintain detailed documentation of their security measures and cybersecurity incidents, so that they can prove compliance in the event of an audit.
Concrete examples
The year 2024 saw several cases illustrating the impact of NIS2 on European businesses. For example, the attack on the Paris mass transit network in February 2024 highlighted the importance of the directive. In response to this attack, RATP had to strengthen its security measures and improve its coordination with ANSSI to minimize the impact and quickly restore services.
How to comply with NIS 2
For companies wishing to comply with the NIS2 directive without blowing their budget or mobilizing too many resources, Parsec represents an ideal solution. By choosing an ANSSI-certified tool, they can strengthen their security while satisfying their customers’ requirements. With its pragmatic approach and controlled costs, Parsec proves that it is possible to combine security, compliance and accessibility.

Conclusion
The NIS2 Directive marks a historic step in strengthening cybersecurity within the European Union. By broadening its scope and introducing stricter security obligations, it aims to protect critical infrastructure and data, and ensure the resilience of essential services against cyber threats. The commitment of member states and the entities concerned will be crucial to the success of this directive, guaranteeing a more secure digital future for all European citizens.
Rapidly evolving technologies and cyber threats require constant vigilance and adaptation of cybersecurity strategies. NIS2 provides a solid framework for meeting these challenges. Its success will depend on the cooperation and commitment of all the players involved. Working together, EU member states must build a secure and resilient digital space, capable of withstanding attacks and protecting the interests of all citizens.





